Note this case contains graphic images from surgery.
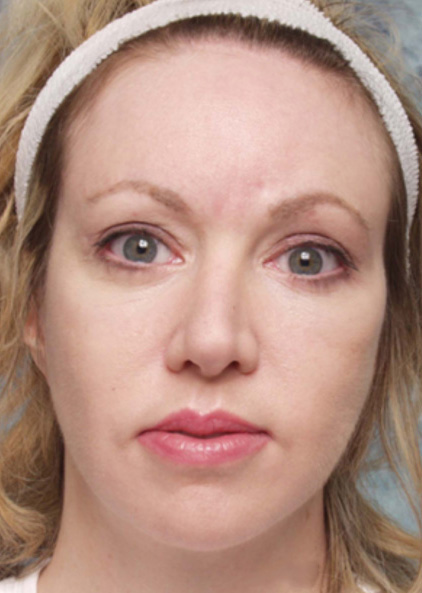
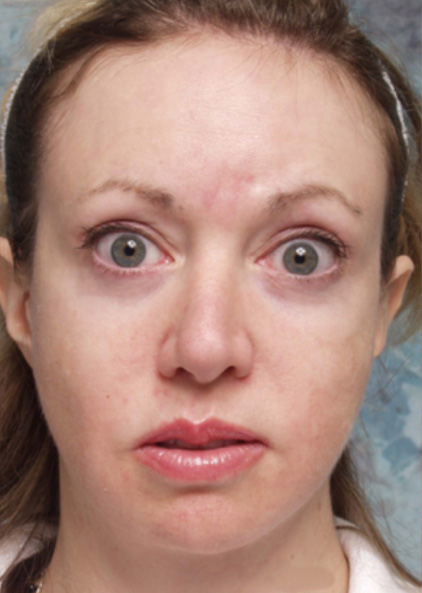
Cosmetic Concern: 34-year old woman with a history of craniofacial surgery for maxillary hypoplasia. To address remaining aesthetic concerns she also had eyelid surgery and several facelifts. However, she feels that she still lacks the projection of her cheekbones that would be best for her face.
Diagnosis:
- Glabellar scar secondary to flap perforation during forehead surgery.
- Bilateral upper eyelid retraction.
- Maxillary hypoplasia with deficient inferior orbital rim. Projection.
- Marked facial asymmetry.
Treatment:
- Augmentation of the orbital rims with custom hand carved orbital rim implant made from ePTFE.
- Vertical midface lift.
- Bilateral lateral canthoplasty
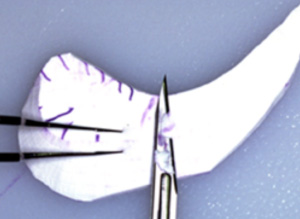
Discussion: The patient needed additional volume in the midface. The ePTFE rim implant is custom carved for her particular anatomic deficit. (Figures A-C)
The outer aspect of the upper eyelids are reattached to the newly formed lateral canthal angle correcting the upper eyelid retraction. Finally, the skin is closed completing surgery.
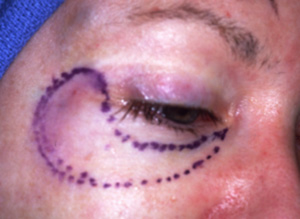
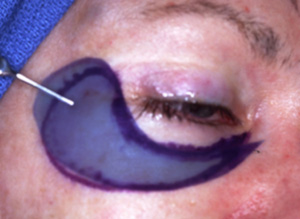
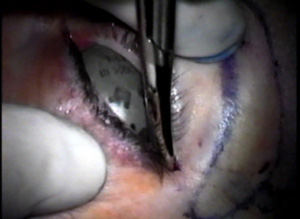
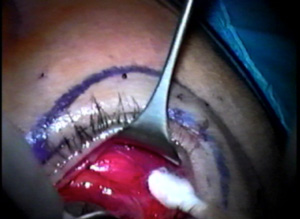
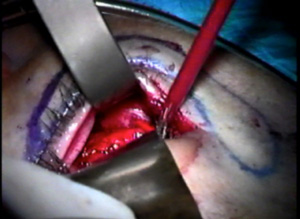
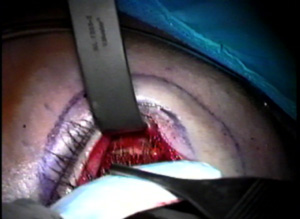
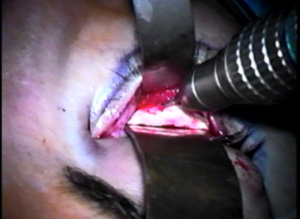
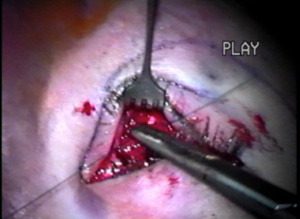
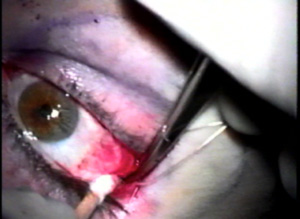
The outer aspect of the upper eyelids are reattached to the newly formed lateral canthal angle correcting the upper eyelid retraction. Finally, the skin is closed completing surgery.
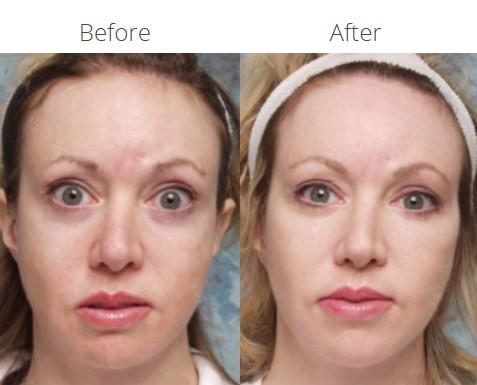
Before
After